引言
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity)是Java连接数据库的的方法;其实本质就是SUN公司定制的一套接口,这样就可以实现Java和各种不同数据库间的连接,如下图:

注:本文使用IDEA示范,数据库使用的是MySQL数据库;
IDEA导入数据库连接Jar包步骤
首先我们要先有对应的MySQL数据库连接驱动jar包,没有的可以评论区找我要;
正常创建一个IDEA项目,如图:
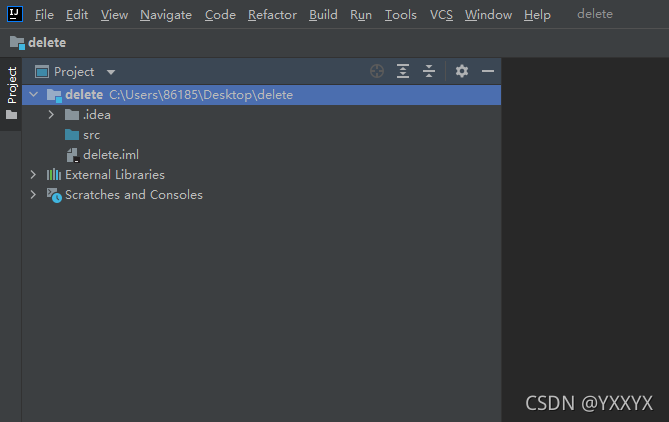
接下来就按图操作导入jar包;
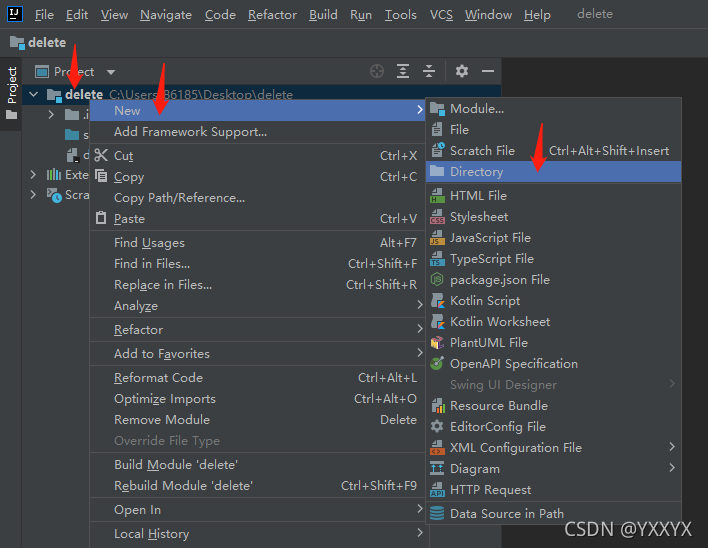
这样我就创建了一个名为lib的文件夹,然后把 mysql-connector-java-8.0.16.jar 粘贴到lib目录下;
如图:
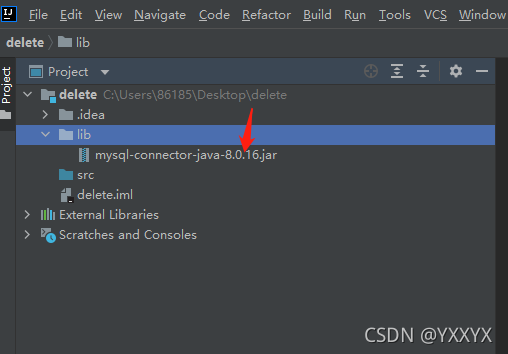
最后一步把jar包导入到项目中,即右键该jar包,再点击Add as Library;
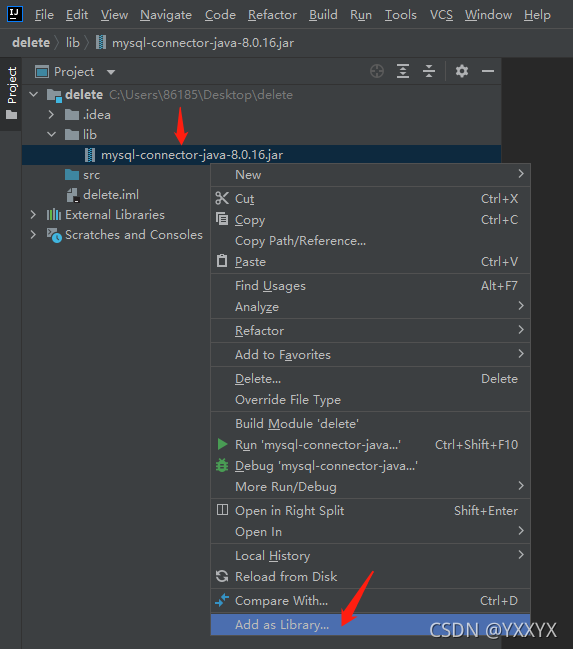
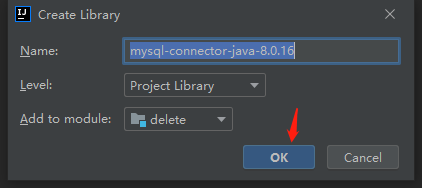
这样就导入jar包了;
接下来就是JDBC的基本操作;
JDBC编程操作
JDBC在Java代码中可以总结为五个操作步骤:
- 注册驱动(确定连接的数据库)
- 获取连接(打开JVM进程和数据库进程之间的通道)
- 获取数据库操作对象(可以用来执行sql语句)
- 执行SQL语句(如果是select查询语句那么需要处理查询结果)
- 释放资源(关闭第二步开启的进程通道)
我自己先创建了一个test02数据库,其中一个表为t_user,如图:
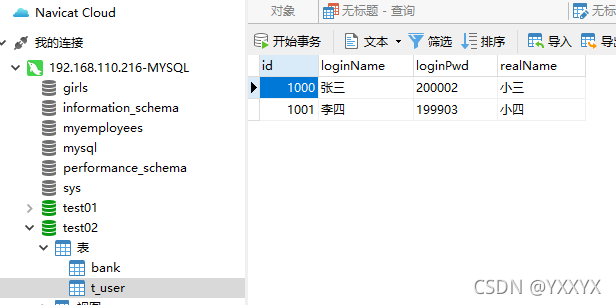
下面就来展示一下使用JDBC实现连接数据库的登录操作(存在问题):
package jdbctest01;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
模拟实现用户登录功能
存在SQL注入问题,不安全;
*/
public class JdbcTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化界面
Map<String, String> userLoginInfo = initUI();
// 验证用户名和密码
boolean loginSuccess = login(userLoginInfo);
System.out.println(loginSuccess ? "登录成功" : "登录失败");
}
/**
* 验证用户名和密码
* @param userLoginInfo 用户登录信息
* @return false表示失败, true表示成功
*/
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
boolean loginSuccess = false; // 标记
String loginName = userLoginInfo.get("loginName"); // 获取用户名
String password = userLoginInfo.get("password"); // 获取登录密码
// JDBC代码
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test02?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "020216");
// 获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 执行sql语句
String sql = "select * from t_user where loginName = '"+ loginName +"' and loginPwd = '"+ password +"'";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 处理结果集
if (resultSet.next()) {
loginSuccess = true;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源(按顺序释放)
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return loginSuccess;
}
/**
* 初始化用户界面
* @return 用户输入的用户名和密码等登录信息
*/
private static Map<String, String> initUI() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// 输入用户名;
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
// 输入密码;
System.out.print("密码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
// 放入map
Map<String, String> userLoginInfo = new HashMap<>();
userLoginInfo.put("loginName", userName);
userLoginInfo.put("password", password);
return userLoginInfo;
}
}
这样就实现了一个登录功能
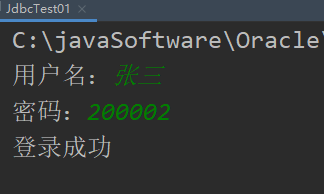
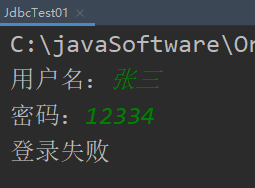
但是这样存在SQL注入问题,SQL注入可以自己搜集资料了解一下,简而言之就是不安全,我示范一下:
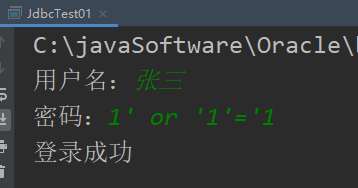
可以看到,张三密码是200002,但是我却可以通过SQL注入语句1' or '1'='1登录成功,这样就存在着很大的问题;
为了解决SQL注入问题,可以使用如下方法:
代码如下:
package jdbctest01;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
解决SQL注入问题
*/
public class JdbcTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> userLoginInfo = initUI();
boolean loginSuccess = login(userLoginInfo);
System.out.println(loginSuccess ? "登录成功" : "登录失败");
}
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
boolean loginSuccess = false;
String userName = userLoginInfo.get("userName");
String password = userLoginInfo.get("password");
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
// JDBC代码
try {
// 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 获取链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test02?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "020216");
// 获取数据操作对象(这里就不同了)?是占位符
String sql = "select * from t_user where loginName = ? and loginPwd = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, userName); // 设置第一个占位符?为username
preparedStatement.setString(2, password); // 设置第二个占位符?为password
// 执行sql语句
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 处理结果集
if (resultSet.next()) {
loginSuccess = true;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return loginSuccess;
}
private static Map<String, String> initUI() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入密码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
Map<String, String> userLoginInfo = new HashMap<>();
userLoginInfo.put("userName" , userName);
userLoginInfo.put("password", password);
return userLoginInfo;
}
}
SQL注入失败:
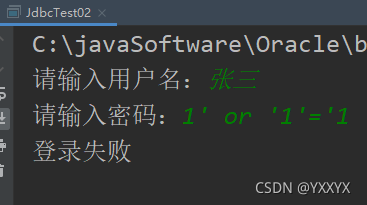
可以发现主要区别是获取数据库操作对象时不再使用Statement,而使用PreparedStatement,这样就可以解决SQL注入问题;所以实际情况下,使用PreparedStatement会更多,还有占位符操作,也很简单,代码中有注释,自己尝试一下就明白了;代码可以多看几遍找找区别;
这就是JDBC最基础的操作,其实就是这几个固定步骤,实在不理解先记住就行了,之后用多了就会明白了;
接下来我们将JDBC的一些操作进行封装;
自定义JDBC工具类
在这里我们将注册、连接、关闭操作封装起来,构成一个工具类;
代码有详细注释;
package jdbctest01.mytest;
import java.sql.*;
/*
JDBC工具类,简化JDBC编程
*/
public class DBUtil {
/**
* 工具类中的构造方法是私有的
* 因为工具类中的方法都是静态的,直接通过类名去调即可。
*/
private DBUtil(){}
/**
* 静态代码块,类加载的时候执行
* 把 注册驱动 程序的代码放在静态代码块中,避免多次获取连接对象时重复调用
*/
static {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test02?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "020216");
}
// 关闭方法
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
这个操作也可以自己实现一下,并不难;
这里值得一提的就是注册驱动放到了静态代码块中,这样就在保证调用的同时避免重复调用;
CRUD操作
对于数据库的操作其实最常用的还是增删改查,但是每次都重写代码实在是复杂,所以这里同样可以自己封装一个增删改查操作;这里还是使用之前的test02数据库,这里是对bank表进行的操作;bank表如图:
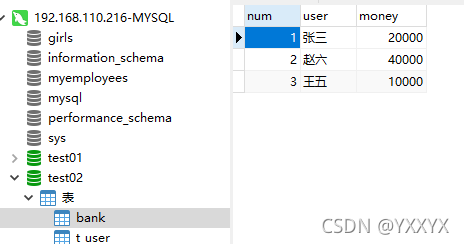
接下来是我自己封装的一个增删改查操作代码(这里使用了DBUtil工具类):
package jdbctest01.mytest;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
// 针对一个表尝试封装增删改查操作
public class CRUD {
/**
* 实现给bank表增加数据的操作
* @param num 主键值
* @param user 用户名
* @param money 存款数目
* @return 返回值为执行sql的数目
* @throws SQLException DBUtil.getConnection()的异常处理
*/
public static int add(int num, String user, int money) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
// 注册驱动并获取链接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 获取数据操作对象
String sql = "insert into bank(num, user, money)values(?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, num); // 第一个占位符?为num
preparedStatement.setString(2, user); // 第二个占位符?为user
preparedStatement.setInt(3, money); // 第三个占位符?为money
// 执行sql语句
int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 执行insert语句
// 释放资源
DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, null);
return count;
}
/**
* 实现bank表的删除操作
* @param num 主键值
* @return 返回执行sql的数目
* @throws SQLException DBUtil.getConnection()的异常处理
*/
public static int delete(int num) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from bank where num = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, num);
int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 执行delete语句
DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, null);
return count;
}
/**
* 实现对bank指定数据的更新
* @param num 主键值
* @param user 用户名
* @param money 存款数目
* @return 返回执行sql的数目
* @throws SQLException DBUtil.getConnection()的异常处理
*/
public static int update(int num, String user, int money) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "update bank set user = ?, money = ? where num = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, user);
preparedStatement.setInt(2, money);
preparedStatement.setInt(3, num);
int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 执行update语句
DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, null);
return count;
}
/**
* 实现对bank表中对应数据的查询
* @param num 主键值
* @return 返回ResultSet值,对应的查询结果
* @throws SQLException DBUtil.getConnection()的异常处理
*/
@Deprecated
public static ResultSet select(int num) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from bank where num = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, num);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 执行select语句
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("num:" + resultSet.getInt("num") +
" user:" + resultSet.getString("user") + " money:" + resultSet.getInt("money"));
}
DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
return resultSet;
}
/**
* 实现对bank表中对应数据的查询
* @param num 主键值
* @return 返回一个Bank类型对象
* @throws SQLException DBUtil.getConnection()的异常处理
*/
public static Bank selectElem(int num) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
Bank bank = new Bank();
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from bank where num = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, num);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 执行select语句
if (resultSet.next()) {
bank.setNum(resultSet.getInt("num"));
bank.setUser(resultSet.getString("user"));
bank.setMoney(resultSet.getInt("money"));
}
DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
return bank;
}
}
这里也要注意到一点:当执行select查询语句时,使用的是executeQuery()方法,而增删改都是使用的executeUpdate()方法;
总结
JDBC其实并没有多少东西,其实总的就是那几步操作,可能刚一接触会有点懵,习惯就好了;
这里还是想提一下:代码只是参考,我希望你可以通过我的代码了解到操作方法,可以自己去创建一个数据库尝试;
当然有问题或者想要相关资源评论区可以留言,希望这篇文章可以给你带来帮助!!!
欢迎大家的点评!
